Arrays vs Linked List
Detailed Differences
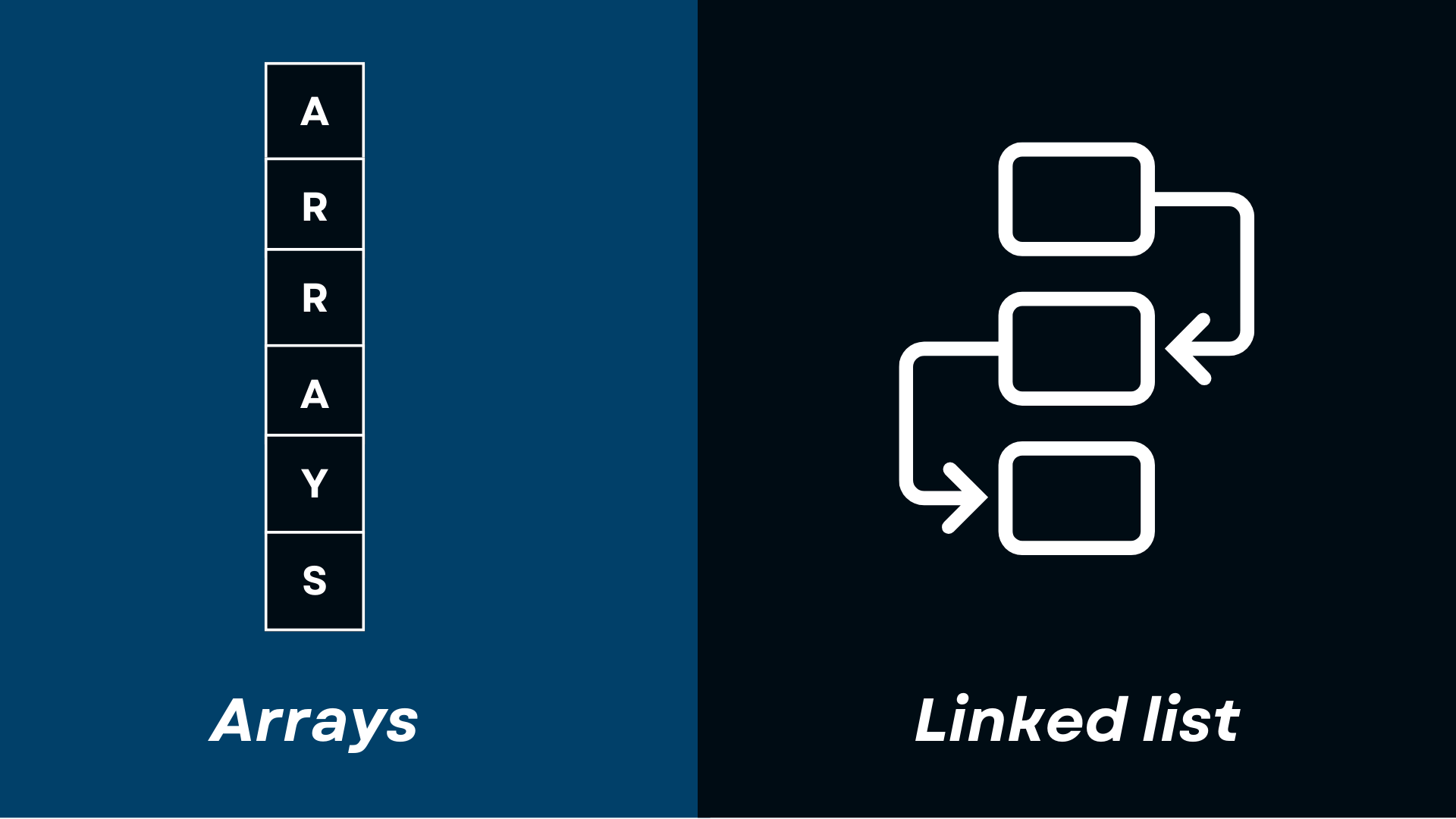
Diagramatic Representation
Array is the sequential representation of a list.
A linked list is the linked representation of list
Advantages of Linked List
- There is no need for an initial size declaration in the case of a linked list because it is a dynamic data structure that can shrink or expand by allocating or deallocating the memory.
- In contrast, in an array, an initial size must be declared, and the number of elements cannot surpass that size, linked list also helps in prevent wastage of memory as only the required number of cells is required.
- A Linked List can be used to easily implement some beneficial data structures such as queues and stacks.
- Insertion and deletion operations in a Linked List are simple because there is no requirement to shift every element after insertion or removal. Only the address in the pointers needs to be changed. We need to shift elements in an array.
Drawbacks of Linked List over Array
- The memory required by a linked list is greater than that required by an array because the linked list contains a pointer field in addition to the data field. Memory is also required by the pointer field to store the address of the next node.
- To access node an at index x in a linked list, folks must first traverse all the nodes preceding it. In the case of an array, however, we can use arr[x] to directly access an element at index x.
- Reverse traversal is not possible in a singly linked list because each node keeps only the address of the subsequent node.
