Mastering SQL: From Fundamentals to Advanced Techniques
Char and Varchar in SQL
Char
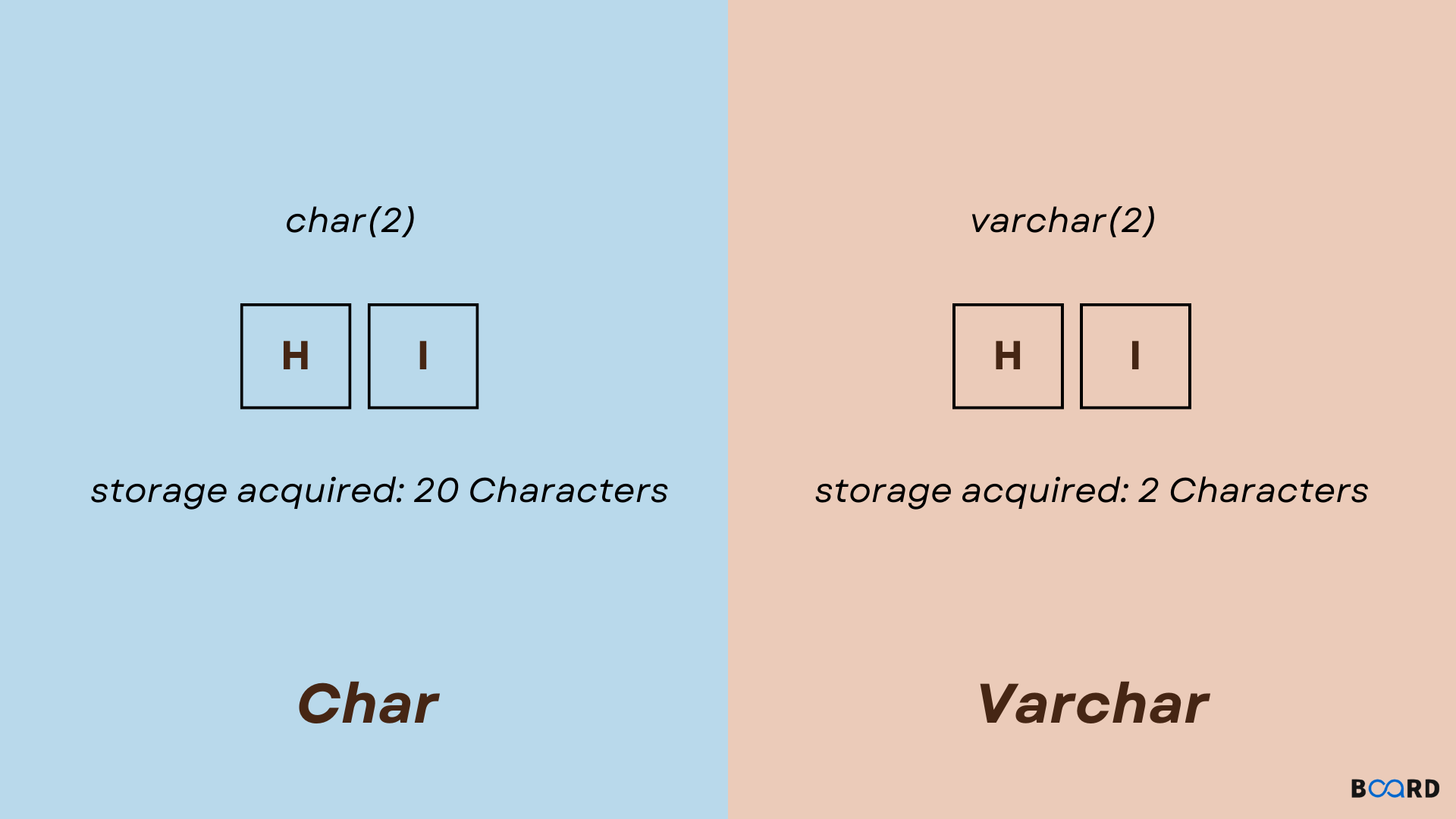
In SQL, it is a kind of data used to hold character strings of a given length. When the PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH_SQL mode is active, if the length of the string is less than the set or fixed length, it is padded with additional blank spaces until it reaches the set length. The CHAR datatype has a storage capacity of n bytes (set length). When we anticipate that all of the data values in a column will be the same length, we should use this datatype.
Example
Consider the query
Output:
Explanation: The output is fixed because the gender column is initiated with length 6.
Varchar
It is a datatype in SQL that is used to record character strings that can be any length up to the maximum allowed. The string won't be padded with additional blank spaces if its length is less than a defined or fixed-length limit. The actual length of the entered string in bytes corresponds to the storage size of the VARCHAR datatype. When we anticipate that the data values in a column may have varied lengths, we should use this datatype.
Example
Consider the following query:
Output:
Explanation: The output is not fixed. The length of Name even though mentioned as 30 during initialization takes length according to the input string.
Difference between char and varchar
Conclusion
VARCHAR conserves space when the length of values varies, while CHAR might do better.
