Cloud Computing Fundamentals: Introduction and Core Principles
Cloud Based Services
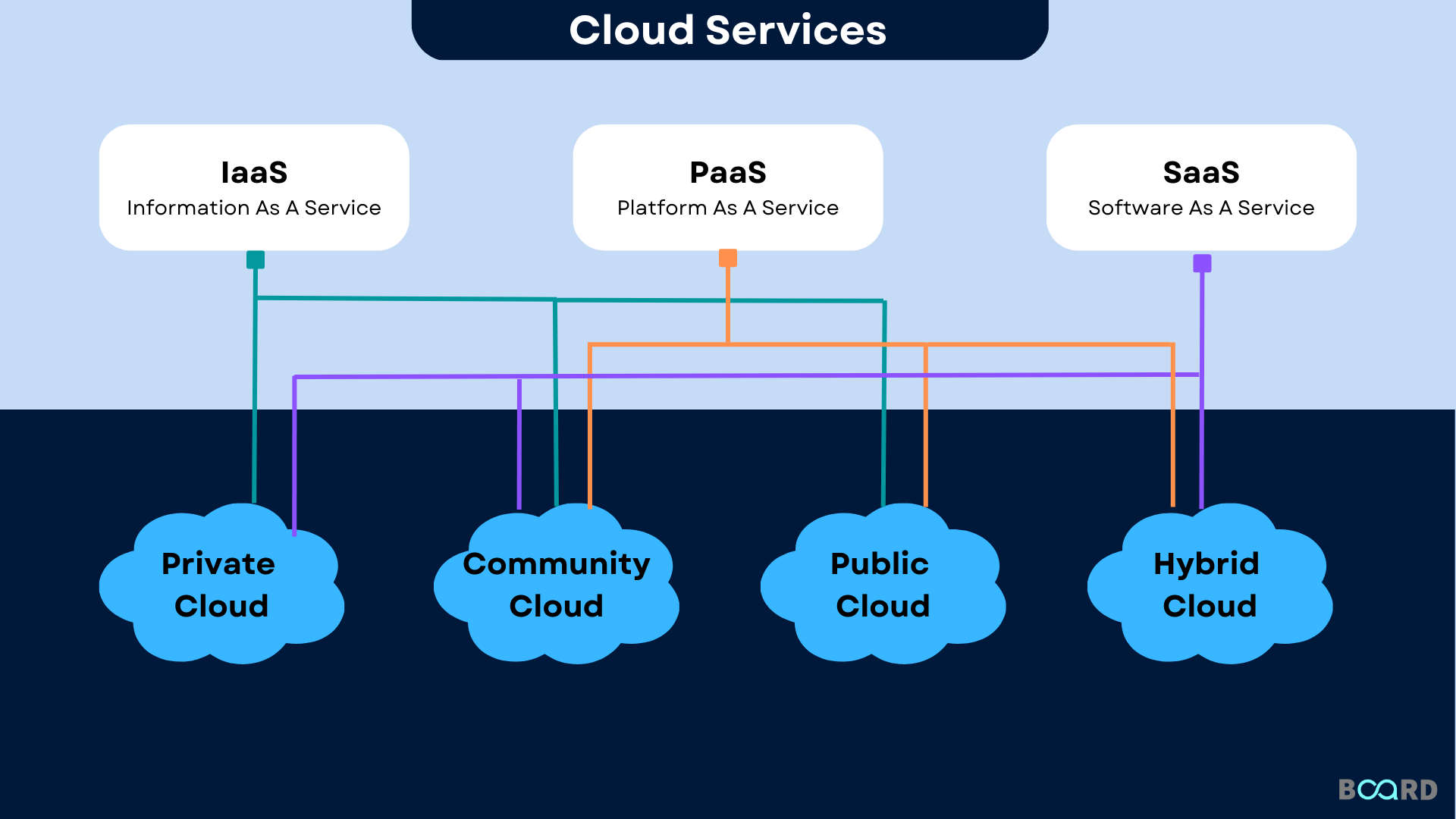
Introduction
Public and private organizations are using information technology differently as a result of cloud computing services. Businesses only pay for the cloud services they actually use to fulfill their IT needs. Although there are many different kinds of cloud computing services, they all share a few fundamental benefits and features. Let us see the 4 major types of Cloud Computing Services in this article.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The more affordable end of managed cloud computing services, when physical resources are given by a third party and maintained on your behalf. Access to computer resources including networking, processing power, and data storage is made available to consumers through IaaS. Without labor-intensive hardware investments or server management, IaaS enables users to use computing power or virtual machines. The cloud service provider manages and maintains all of the networks, servers, and data centers from which the hardware resources are physically sourced.
By using IaaS, a user may access a Linux system, for instance, without having to worry about the physical system or the connectivity of the machine on which Linux is installed. For clients who want to build highly scalable, cost-effective IT solutions, IaaS is advantageous because it lets a service provider handle the costs and hassles of managing physical resources. While customers are in charge of installing and maintaining databases, operating systems, applications, and security components, the majority of IaaS packages also contain servers, networking, memory, and virtualized components.
Examples of cloud computing IaaS services include:
Amazon EC2, Windows Azure, Rackspace, Google Compute Engine.
IaaS Characteristics and advantages
- A conventional IaaS offering saves time and money since the service provider sets up and supports the underlying hardware.
- Resources are made accessible as and when they are needed, preventing the wasting of any unused ones and the delays in adding new ones.
- Pay solely for the resources you really use, or a utility-based pricing strategy.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
IaaS has evolved into this cloud computing service. PaaS offers the computing environment and solution stack as a service in addition to providing the IT infrastructure. PaaS is a cloud computing service that offers programmers a foundation for creating unique apps. Software developers may create unique web applications using Platform as a Service without having to worry about managing, serving, or storing data.
PaaS core includes:
Design and development software for hosting solutions. Server-side scripting environment Support for DBMS Network Access Storage Server
Examples of cloud computing services using PaaS
Microsoft Azure, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Force.com. by Salesforce, Google App Engine, Rackspace Cloud Sites, OpenShift, and Apache Stratos
PaaS - Features and advantages
- Because anybody can create an application using an one click feature in a web browser, PaaS makes software development simple even for non-experts.
- Since the PaaS service provider takes care of all the update patches, upgrades, and routine software maintenance, users don't need to upgrade or update the infrastructure.
- Because developers from many places may collaborate on the same application development using PaaS, geographic freedom is provided.
- Investments in the actual infrastructure or the necessary management skills are not necessary; SAP is one such example. The option to rent virtual IT infrastructure offers users significant cost savings.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
IaaS and PaaS service offerings combined into one unique cloud computing solution. SaaS, or software as a service, is a type of cloud computing that offers application-level services suited to various company needs, such as marketing automation, CRM, or business analytics. SaaS, or software as a service, is a cloud computing service that offers customers web-based software applications on demand. SaaS companies host fully functional applications with browser-based user interfaces and make them available to users online.
As the applications operate on the vendor's servers, SaaS options enable the cloud to be used for software architecture, lowering the cost of support, maintenance, and operations. Since customers frequently engage directly with SaaS apps like Netflix, Gmail, JIRA, Dropbox, or Salesforce, SaaS is the most well-known cloud computing service offering. SaaS, or software as a service, allows consumers to subscribe to software on a monthly basis as opposed to buying it outright, saving them money up front. Additionally, it gives consumers the option to cancel their subscriptions when they are no longer required.
SaaS cloud computing services examples:
SAP Business ByDesign, Zoho CRM, AppDynamics, Microsoft Office 365, Pardot Marketing Automation.
SaaS characteristics and advantages
- Since customers may start using the programme as soon as they subscribe, there is no upfront setup fee.
- Since the service provider provides the computing power, there are no hardware costs either.
- As consumers pay for the services using a pay-as-you-go mechanism, there are flexible payment options.
- The programme is automatically updated, and updates are always free. Because SaaS apps may be accessed through any internet-enabled device, whether a laptop, smartphone, or desktop,
- SaaS offers cross-device compatibility. Businesses do not need to hire an IT specialist to install the programme on a variety of workstations or worry about keeping the software current on every PC.
Functions as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS is a brand-new and still-emerging cloud computing service that is revolutionizing numerous industries. Software developers may create and deploy apps using the serverless computing paradigm without having to think about server operations. Google Cloud Function, Microsoft Azure Functions, Webtask.io, Iron.io, Open Whisk, and AWS Lambda are a few examples of FaaS.
FaaS - Features and Benefits
- Since users are charged according to the quantity of functionality used, money is never lost on unused resources.
- Makes developers more effective since they can concentrate on building logic relevant to each application rather than having to worry about server administration.
- Code written for FaaS is scalable and fault-tolerant by nature.
Conclusion
Depending on their needs, areas of expertise, operational procedures, and other considerations, businesses can embrace one or more cloud computing services. Make sure to conduct adequate study to comprehend company requirements before selecting a cloud computing service provider. Locate service providers who can deliver the needed cloud solutions that are completely functional depending on the specifications.
