Cloud Computing Fundamentals: Introduction and Core Principles
Cloud Computing Virtualizations | Types of Cloud Computing Virtualizations
Introduction
The idea of virtualization in computers has been around for more than 60 years. Now, cloud service providers offer customized, user-centered virtual environments on demand. All of the processing and storage hardware for these environments is housed on a single physical cloud server. These environments appear localized to the users who interact with them.
Various Virtualization Techniques in cloud computing
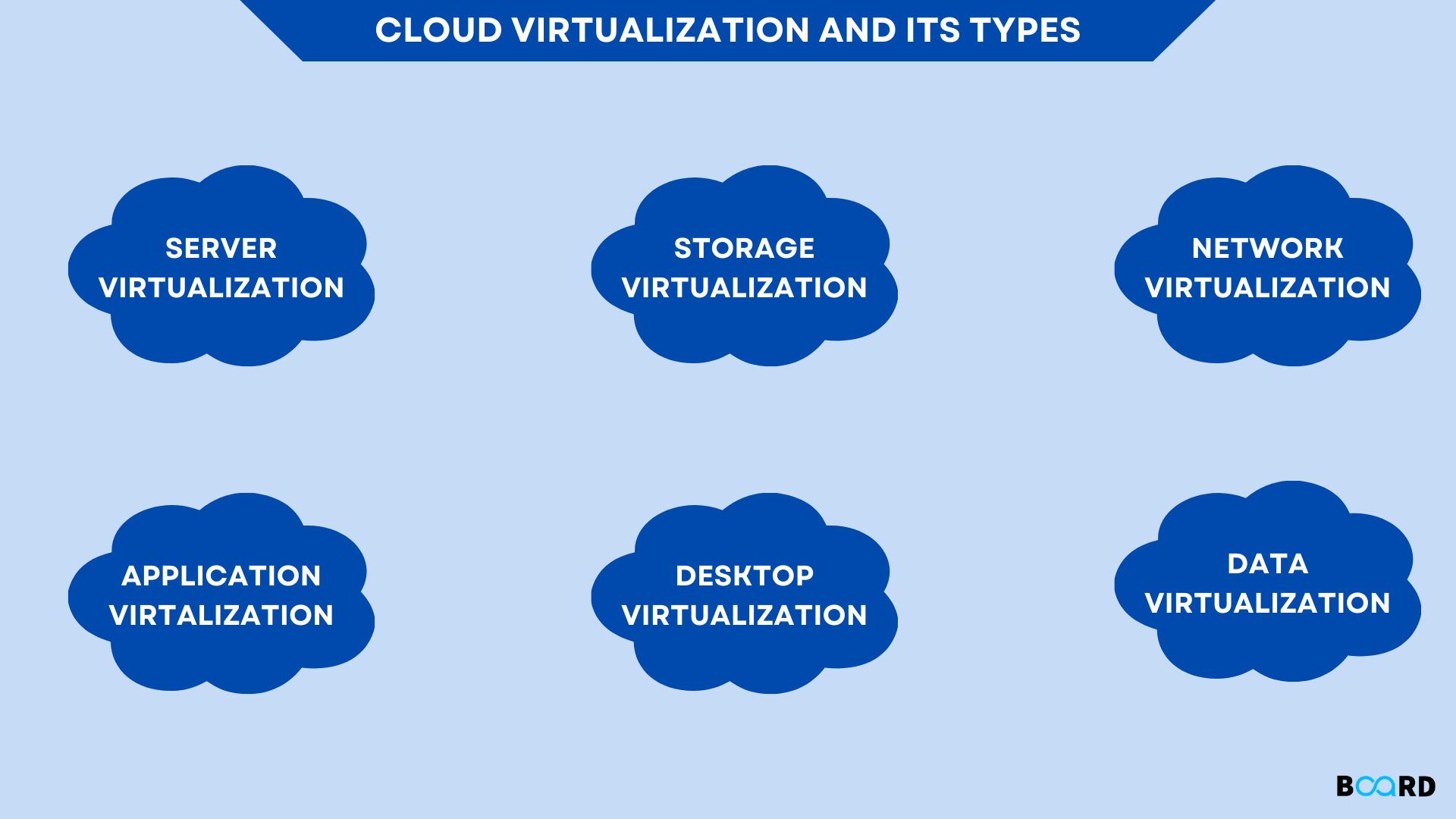
We've seen what virtualization is as a computing technique so far, as well as how cloud computing makes use of its tenets. Let's now examine the various forms of virtualization used in cloud computing with a closer look at their specifics.
1. Server Virtualization
The underuse of hardware computer resources was a major factor in the need for virtualization. The term "server virtualization" refers to the division and network distribution of a server's hardware, software, and networking resources. Virtual servers are another name for these divisions. Because users may request different combinations of storage, processing power, RAM, etc. from the real server, server virtualization enables flexible scaling.
When customers wish to set up many operating systems on one assembly of computer components, virtualizing a server is useful. Installing hypervisors on a server is the first step in virtualizing it. Hypervisors may be thought of as a layer between a host machine's physical parts (in this example, the server) and the software that will be placed on it. Both of these hypervisors—Type 1 and Type 2—can be installed directly on a server or on top of an already-existing operating system (Type 2).
2. Storage Virtualization
In order for storage virtualization to function, many physical storage arrays must be gathered and combined before being presented to the user as a single storage location through a network. Organizations and individuals that want to increase and manage the storage on their systems without spending money on actual storage devices frequently use it. On a user's system, virtualized storage appears as a single storage object (like a 2 TB disc drive). However, in order to provide the customer with 2 TB of storage, storage virtualization pools numerous storage sites.
Benefits:-
- By concealing the specific hardware/software settings of each storage device, it enables central administration of all of them.
- Users may flexibly scale their storage capacity thanks to it.
- By placing a lot of important data in one place, it enables enterprises to manage it.
- Consolidating data at a single storage location makes backing up, recycling, and discarding data simpler.
- Better storage performance is available by virtualizing storage at significantly lower costs.
- Another remarkable aspect of storage virtualization is automated management.
- A large portion of the burden of storage management for IT teams is removed by automated storage management.
3. Network Virtualization
Earlier, we observed how heterogeneous storage pools are combined into a single storage location using storage virtualization. Similar functions are performed by network virtualization, but with some modifications. Network virtualization is the process of combining all network components and managing them solely through software. All of the network's supporting hardware and software, along with each one's unique functionalities, are included in these network components.
A network becomes a virtual network when its reliance on the software present in the hardware supporting it is removed. Although the network is still using its hardware resources, the functionality and availability are now controlled by the virtualizing software, which is comparable to a hypervisor. Network virtualization is frequently used to connect virtual networks, combine multiple networks into one, or divide a network's resources. Networks that have been virtualized are more flexible and enable more efficient networking at lower costs.
4. Application Virtualization
Currently, we must first install a computer application on our device before we can use it. But what if we never again needed to install that application—or any other application, for that matter? What if we could easily access cloud-based programs whenever we needed them, and they would function just like their local equivalents? Application virtualization puts forth this concept. Using a network to install a computer program is known as "application virtualization" (the cloud). When a user requests the deployed application, an instance of the program is shown to them on a server where it is locally installed. The user may then interact with the program as though it were already downloaded on their computer.
- The majority of the difficulties of installing apps locally are eliminated by the effective notion of application virtualization.
- Users may access a variety of programs in real-time using this without having to provide each one with a lot of storage space.
- Users can also use programs that are not supported by the operating systems of their devices.
- Not to mention that IT staff no longer need to manage and update several programs across various operating systems.
5. Desktop Virtualization
Application virtualization and desktop virtualization are related, but with the former, whole desktop environments are used in lieu of the programmes. The desktop environments, also known as virtual machines (VMs), are kept on strong servers that can support several concurrent desktop sessions. Regardless of the capabilities of their devices, users can access these VMs on them as needed. Because it provides all employees with an uniform desktop experience, desktop virtualization is particularly helpful for businesses.
The management and distribution of updates for a company's devices may now be done centrally by IT staff. The security hazards related to employees keeping corporate data locally are also reduced by virtual desktops. Additionally, since the majority of the data is kept on servers, a device failure won't cause a significant loss.
6. Data Virtualization
Storage virtualization is a solution to the data management issue of combining and analysing data from several sources quickly. While providing a comprehensive picture (single view) of the data, it enables enterprises to centrally manage and modify data from several sources, like excel files, Google Analytics reports, HubSpot reports, etc. By isolating the acquired data from the underlying data logic, data virtualization operates. Between the data's source and its front-end use, a virtualization layer known as a data virtualization tool mediates.
By virtualizing data, users may access the original data source in real-time and examine heterogeneous data sets as a group through a single interface. Data virtualization is mostly employed in fields like BI (business intelligence), Cloud computing, and of course, data management as a component of data integration.
Conclusion
Although virtualization is a fairly old idea, the combination of cloud computing and virtualization has fundamentally altered how the tech community views it. It is now possible to share entire IT infrastructures using what was once thought of as a tool for sharing resources. You can use it to lower costs, boost effectiveness and productivity, or ease IT management issues.
