

International Business Machines Corporation (IBM), commonly known as IBM, is a prominent American multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York. Founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company, it was renamed IBM in 1924. Over the decades, IBM has been at the forefront of technological innovation, notably in the development of the mainframe computer, the personal computer, and artificial intelligence with its Watson platform. With a presence in over 175 countries, IBM is recognized as the largest industrial research organization globally, holding a record for the most annual U.S. patents for nearly three decades, reflecting its commitment to research and development in computing technology.
This blog is designed to provide comprehensive insights into IBM’s operations, culture, and recruitment process, equipping aspiring candidates with the knowledge and tools they need to succeed in securing a role at this global giant.
1. IBM Overview
About
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Founder |
George Winthrop Fairchild Charles Ranlett Flint Herman Hollerith |
| Industry Type | Information Technology |
| Founded | 1924 |
| Headquarters | New York, USA |
History
Early Years (1880s - 1924): Origins and Formation
- 1885: Julius E. Pitrap patents the computing scale.
- 1888: Alexander Dey invents the dial recorder.
- 1889: Herman Hollerith patents the Electric Tabulating Machine, and Willard Bundy invents the time clock.
- 1911: Charles Ranlett Flint amalgamates the four companies into the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR) in New York.
- 1914: Thomas J. Watson, Sr. joins CTR as General Manager and later becomes President. Watson introduces pioneering sales tactics.
- 1924: CTR officially renames itself International Business Machines (IBM).
Growth and Global Expansion (1924 - 1950s)
- 1928: IBM punch cards become the industry standard, notably used in the US Census.
- 1933: IBM merges its subsidiaries, consolidating operations into one company.
- 1943-1945: IBM contributes to the WWII effort by producing M1 Carbine rifles and manufacturing tabulating equipment used by Nazi Germany.
- 1952: IBM introduces magnetic tape data storage, marking the transition from mechanical calculators to electronic computers.
Innovation and the Mainframe Era (1950s - 1980s)
- 1956: Arthur L. Samuel demonstrates the first example of artificial intelligence, programming an IBM 704 to play and learn checkers.
- 1957: IBM introduces the FORTRAN programming language.
- 1961: IBM develops the SABRE reservation system for American Airlines.
- 1964: IBM launches the System/360, the first computer system family, which revolutionized business computing by allowing upgrades without rewriting applications.
- 1969: IBM provides guidance computer hardware for the Apollo 11 mission, helping land the first men on the moon.
- 1970: IBM releases the System/370, which along with System/360 becomes the dominant mainframe computer.
- 1974: IBM engineer George Laurer develops the Universal Product Code (UPC) barcode.
- 1981: IBM introduces the IBM PC, a standard in the personal computer industry.
Challenging Times and Restructuring (1980s - 1990s)
- 1991: IBM begins spinning off divisions into autonomous subsidiaries, including AdStar, Lexmark, and others.
- 1993: IBM posts an $8 billion loss, the largest in American corporate history, leading to the hiring of Lou Gerstner as CEO.
- 1997: IBM's Deep Blue supercomputer defeats chess champion Garry Kasparov, marking a milestone in AI development.
Technological Advancements and Strategic Acquisitions (2000s - 2010s)
- 2002: IBM acquires PwC Consulting.
- 2009: IBM receives the National Medal of Technology and Innovation for its Blue Gene supercomputing program.
- 2011: IBM's Watson AI defeats champions on "Jeopardy!" and garners worldwide attention.
- 2014: IBM sells its x86 server division to Lenovo.
- 2015: IBM makes major acquisitions, including Merge Healthcare, Cleversafe, and The Weather Company's digital assets.
- 2019: IBM completes its $34 billion acquisition of Red Hat, marking one of its largest deals ever.
Modern Era: Cloud, AI, and Beyond (2020 - Present)
- 2020: IBM announces plans to spin off its Managed Infrastructure Services into a separate company, later named Kyndryl.
- 2021: IBM unveils the world’s first 2-nanometer chip, pushing the boundaries of semiconductor technology.
- 2023: IBM acquires Manta Software to bolster its AI and data governance capabilities and announces plans to acquire Software AG's StreamSets.
Key Milestones in IBM’s History:
| Year | Event Description |
|---|---|
| 1928 | IBM punch cards become the industry standard for the next 50 years, holding nearly all of the world’s known information and enabling large-scale projects like the US Census. |
| 1952 | IBM introduces the world to digital storage via magnetic tape data, marking the transition from punched-card calculators to electronic computers. |
| 1956 | Arthur L. Samuel programs an IBM 704 to play checkers and learn from its experience, considered the first demonstration of artificial intelligence. |
| 1969 | IBM builds the computers and software for the Apollo missions, successfully landing Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin on the moon and guiding them back to Earth. |
| 1997 | IBM’s Deep Blue supercomputer defeats the world’s best chess player, marking a giant leap forward for artificial intelligence. |
| 2021 | IBM introduces the world’s first 2-nanometer chip with 50 billion transistors, holding the potential for greener data centers and safer autonomous vehicles. |
2. Company Culture and Values
IBM's culture formula brings the company's work experience to life.
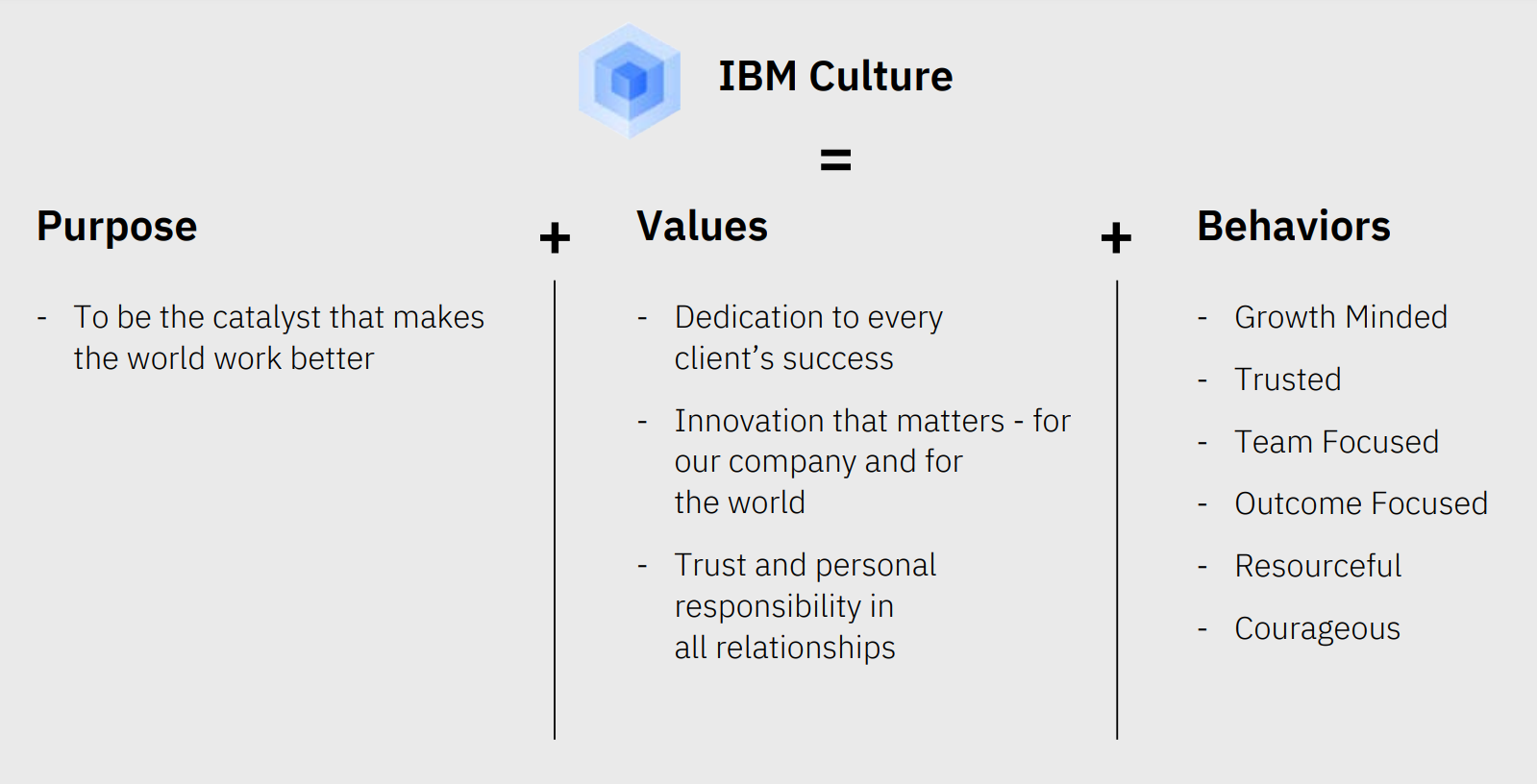
Purpose
IBM strives to make a lasting, positive impact on the world by upholding strong business ethics, protecting the environment, and supporting the communities in which its employees work and live.
Core Values of IBM
Guided by three fundamental values, these principles shape IBM's culture and brand:
2. Innovation that matters - for the company and for the world
3. Trust and personal responsibility in all relationships
Growth Behaviour
IBM's Growth Behaviors outline how employees engage with each other, clients, and partners, driving the company's commitment to excellence and collaboration.

3. Comprehensive Product and Service Offerings
Software
AI and Machine Learning
- IBM Watson
- Watsonx
- Machine learning tools
Analytics
- IBM Cognos Analytics
- SPSS
- Data visualization tools
Data Management
- Db2 database management system
Middleware
- IBM WebSphere
- IBM MQ
Security Software
- IBM QRadar
- MaaS360
Hardware
Mainframe Computers
- IBM z Series (e.g., z16)
Microprocessors
- Power Microprocessors
- TrueNorth chip
Storage Solutions
- IBM FlashSystem
- IBM Storwize
- Tape storage products
Services
Consulting Services
- IBM Global Business Services
- Technology consulting
Support Services
- IBM Technology Support Services for hardware and software
Cloud Services
- IBM Cloud (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- IBM Bluemix
Applications
- Business Applications: Industry-specific solutions leveraging AI and analytics
- Development Tools: Tools for application development and deployment
Services Assets
- AI Models: Pre-trained models for various applications
- Cloud Infrastructure: Hybrid cloud solutions for businesses
Data Sets
- Training Data Sets: Curated datasets for AI and machine learning applications
- Industry Data: Sector-specific data for analytics and AI applications
Additional Products
- Blockchain: Solutions for secure transactions and data integrity
- Business Operations: Tools for optimizing business processes
- Cybersecurity: Security solutions for data protection and compliance
- Data Storage: Solutions for efficient data storage and retrieval
- IT Infrastructure: Hardware and software for robust IT environments
- Quantum Computing: Research and development in quantum technologies
- Software Architecture: Frameworks and tools for software development
Solutions Offered
- Automation: Tools for automating business processes
- Data and AI: Solutions combining data management with AI capabilities
- Industry Solutions: Tailored solutions for specific industries
- Infrastructure: Robust IT infrastructure solutions
- Security: Comprehensive cybersecurity offerings
- Sustainability: Solutions aimed at promoting sustainable practices
4. Financial Performance and Market Position
Bank Stock Performance
Financial Metrics Table
5. Competitors of IBM
IBM faces competition from several major companies across different sectors. Here are five of its top competitors, along with an overview of their services and market positions:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Overview: AWS is a subsidiary of Amazon providing on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis.
- Services: AWS offers a wide range of cloud services, including computing power, storage options, and networking capabilities. It also provides machine learning, analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) services.
- Market Position: AWS is a leader in the cloud computing market, holding a significant share and continuously innovating to maintain its competitive edge against other cloud service providers.
2. Microsoft Azure
- Overview: Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service created by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.
- Services: Azure provides a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including virtual machines, app services, databases, and AI capabilities. It also supports various programming languages and frameworks.
- Market Position: Azure is one of the top cloud service providers, consistently competing with AWS for market leadership and expanding its services to meet diverse business needs.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Overview: GCP is a suite of cloud computing services offered by Google, providing a range of hosted services for computing, storage, and application development.
- Services: GCP includes services such as Google Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, and BigQuery for data analytics. It also offers AI and machine learning tools.
- Market Position: GCP is a significant player in the cloud market, known for its data analytics and machine learning capabilities, and is continuously striving to increase its market share.
4. Oracle Corporation
- Overview: Oracle is a multinational computer technology corporation that offers software, cloud solutions, and hardware products, primarily focusing on database software and technology.
- Services: Oracle provides cloud services, database management systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, and customer relationship management (CRM) solutions.
- Market Position: Oracle is a strong competitor in the enterprise software and cloud services markets, particularly known for its database solutions and cloud infrastructure offerings.
5. Accenture
- Overview: Accenture is a global professional services company that specializes in consulting, technology services, and outsourcing.
- Services: Accenture offers a wide range of services, including strategy and consulting, digital transformation, technology implementation, and managed services across various industries.
- Market Position: Accenture is a leader in the consulting space, competing with IBM’s Global Business Services, and is recognized for its innovation and ability to drive digital transformation for clients.
These competitors highlight the diverse landscape in which IBM operates, each excelling in different areas such as cloud computing, software solutions, and consulting services.
6. Recruitment Process at IBM
IBM's recruitment process is structured to ensure a thorough evaluation of candidates while promoting diversity and inclusion. Here’s an overview of the process and the types of assessments involved:
Recruitment Process
- Application Submission: Candidates start by finding a role of interest and completing their application online. Joining the Talent Network is recommended to stay connected.
- Resume Screening: Applications are reviewed by IBM professionals who specialize in the relevant fields.
- Online Assessments: Candidates may be asked to complete online assessments that vary depending on the role applied for. These assessments are scientifically validated to be engaging and relevant.
- Interview Process: Successful candidates may be invited for interviews or to participate in an Assessment Center. Interviews can be conducted via phone, video, or in-person, and may involve multiple interviewers.
- Feedback and Updates: Candidates receive regular updates on their application status, and feedback is available upon request after interviews.
- Onboarding: If selected, candidates receive documentation to complete their onboarding process.
Types of Online Assessments
- Coding Challenges: Candidates may be presented with a coding interface to solve programming challenges, helping assess their programming knowledge and abilities.
- Interview Assessments: These involve a series of interview questions, where responses are captured via webcam and microphone, allowing IBM to evaluate candidates' skills and fit for the role.
- English Proficiency Assessment: A text-based assessment with multiple-choice questions to evaluate candidates' English language skills.
This structured approach reflects IBM's commitment to a fair and engaging recruitment experience while prioritizing diversity and inclusion throughout the hiring process.
For more information, visit IBM.
7. IBM's Learning and Development Opportunities
IBM offers a range of learning and development opportunities aimed at empowering employees to direct their career paths and build necessary skills. Here are the key components of IBM's learning and development initiatives:
Performance Reflections
- Twice annually, IBMers participate in performance reflections, allowing them to celebrate accomplishments and identify focus areas for future growth. This process involves evaluations based on business outcomes and skills, with managers actively engaging in discussions with employees.
Learning Resources
- Your Learning at IBM: This platform generates personalized learning recommendations and resources for employees using IBM Watson® AI technology, enabling tailored learning experiences.
- Your Career at IBM: Designed to help employees assess their current skills, identify skills needed for new roles, and find career opportunities within the company. It connects employees to certification programs, coaching, and mentoring.
Focus on Skills Growth
- IBM's learning strategy emphasizes skills development and aligns with the company's goals for internal mobility. The refreshed learning programs aim to accelerate skills growth in a more efficient and personalized manner, allowing for deeper learning in less time.
Average Learning Hours
- IBM encourages its employees to engage in learning, with an average of 85 hours of learning per regular, full-time employee annually.
These initiatives reflect IBM's commitment to fostering a culture of continuous learning and development, ensuring that employees have the tools and resources necessary to succeed in their careers.
For more information, visit IBM.
8. Future Outlook and Strategic Plans
IBM's future outlook and strategic plans focus on enhancing its position in the hybrid cloud and artificial intelligence (AI) markets. Here are the key elements of IBM's strategic direction:
Strategic Focus Areas
- Hybrid Cloud and AI Capabilities: Under CEO Arvind Krishna, IBM is committed to a "maniacal focus" on its open hybrid cloud platform and AI technologies. This strategy aims to capitalize on the growing client demand for these capabilities, positioning IBM as a leader in these transformative areas.
- Separation of Managed Infrastructure Services: IBM has spun off its managed infrastructure services business into a new independent company, referred to as "NewCo." This move allows IBM to concentrate on its core strengths in hybrid cloud and AI, while NewCo focuses on delivering managed infrastructure services.
- Growth Potential: Analysts predict that IBM's annual revenue could reach nearly $78 billion by 2028, up from approximately $61.9 billion in the previous year. This growth is expected to be driven by the expanding hybrid cloud market, which is projected to grow at a rate of 22% annually through 2029.
- Financial Performance: IBM has shown signs of financial recovery, with improvements in operating cash flow and free cash flow. The company aims to leverage its hybrid cloud and AI strategies to enhance profitability and shareholder value.
- Client-Centric Approach: IBM emphasizes a relentless focus on client success, which is seen as essential for driving growth. The company aims to innovate and respond quickly to client needs, ensuring that it remains relevant in the rapidly evolving technology landscape.
IBM is strategically positioning itself to harness the growth opportunities in hybrid cloud and AI. By focusing on these areas and separating its managed infrastructure services, IBM aims to enhance its operational efficiency and drive sustainable growth in the coming years.
9. Conclusion
IBM stands at the forefront of technological innovation, continually evolving to meet the demands of a dynamic market. With a strong emphasis on hybrid cloud and artificial intelligence, the company is strategically positioned to leverage these growth areas for future success. IBM's commitment to employee development through personalized learning programs and performance reflections fosters a culture of continuous improvement. As it navigates competition from major players in the tech industry, IBM's focus on client-centric solutions and sustainable practices ensures it remains a key player in shaping the future of technology and business transformation.
Key Takeaways for Aspiring IBM Candidates:
- Understand the Recruitment Process: IBM's recruitment involves multiple stages, including a cognitive ability assessment, coding round, technical interview, and HR interview. Candidates must clear each round to receive a job offer.
- Prepare for Technical Assessments: Candidates should focus on honing their technical skills, particularly in programming languages like Java or Python, and be well-versed in data structures, algorithms, and relevant technical concepts.
- Practice Aptitude and Reasoning: The written test typically includes sections on logical reasoning, quantitative aptitude, and verbal ability. Effective preparation through mock tests can enhance performance in this critical stage.
- Demonstrate Soft Skills: IBM values communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities. Candidates should prepare to showcase these skills during interviews, particularly in behavioral questions.
- Research and Align with IBM’s Values: Understanding IBM's culture and values is essential. Candidates should be prepared to articulate why they want to work for IBM and how their goals align with the company's mission and vision.
By focusing on these key areas, aspiring candidates can significantly enhance their chances of securing a position at IBM, one of the world’s leading technology companies.
