Mastering SQL: From Fundamentals to Advanced Techniques
GROUP BY in SQL
Introduction
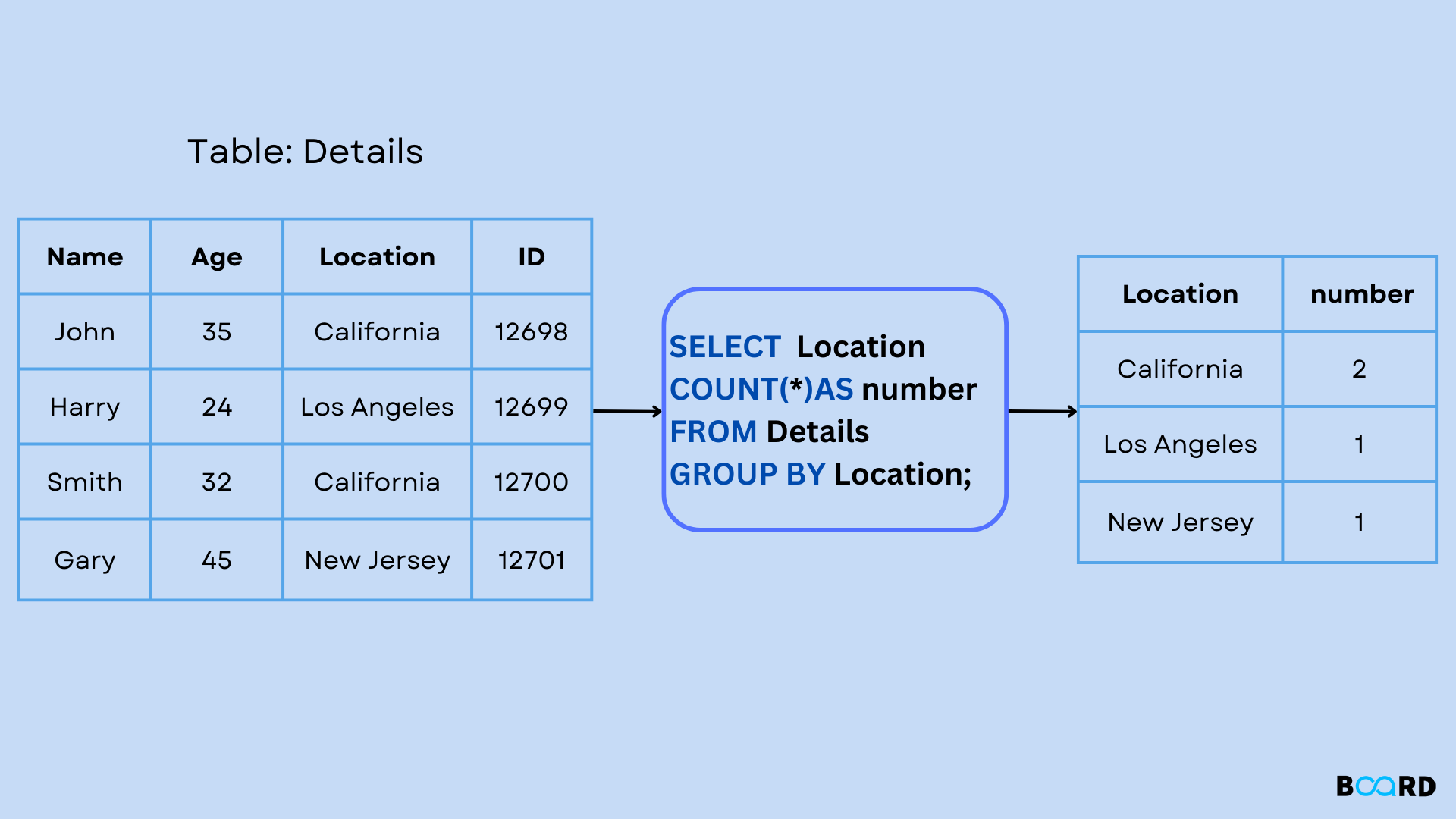
Finding summary rows, such as "find the number of consumers in each country," is done with the GROUP BY statement, which groups rows with similar values.
The COUNT(), MAX(), MIN(), SUM(), and AVG() aggregate functions are frequently used with the GROUP BY statement to group the result set by one or more columns.
Syntax
In the following code block, a GROUP BY clause's fundamental syntax is displayed. If there is an ORDER BY clause, it must come after the GROUP BY clause and come before the constraints in the WHERE clause.
Demo Database:
Here are some examples from the Northwind sample database's "Customers" table:
SQL GROUP BY Examples
The SQL query that follows provides a breakdown of the number of clients by nation:
Output:
The clients in each country are listed in the following SQL query, from most to least:
Output:
Demo Database:
Here is an excerpt from the Northwind sample database's "Orders" table:
A choice from the "Shippers" table is as follows:
Example of GROUP BY with JOIN
The SQL query that follows provides a list of the orders that each shipper has sent:
Output:
