Mastering ReactJS: Understanding Hooks, Components, and Libraries
Understanding setState in Reactjs
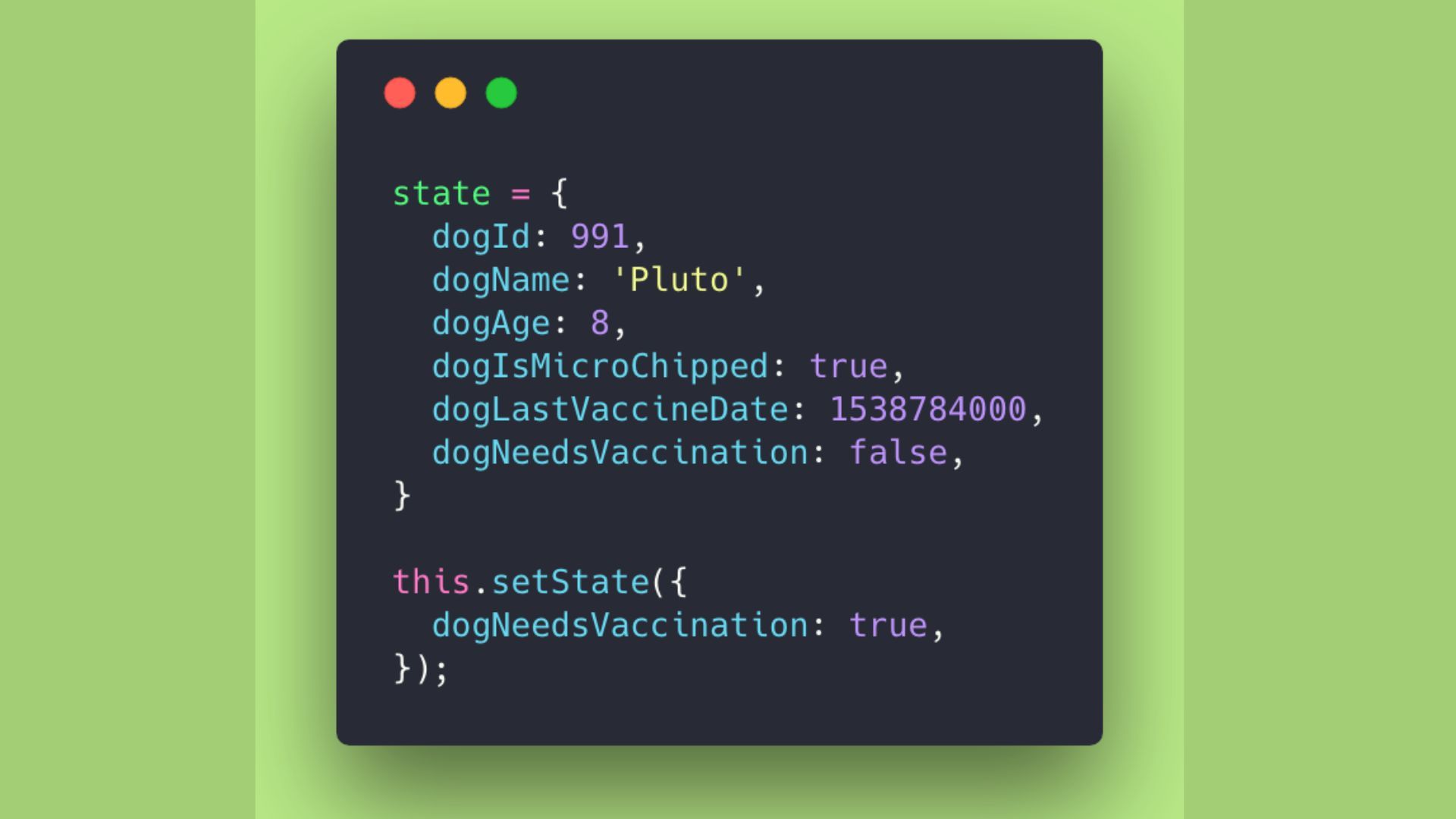
What Is 'State' in ReactJS?
A state is a component object built into React that contains data or information. Throughout the life cycle of a component, its state can change; re-rendering occurs whenever the state changes.
A change in state can occur as a result of user interaction or system events, and it determines how the component behaves and renders.
The setState() Method
Depending on the event handler, the server response, or the property change, the state can get updated. The setState() method does this.
The setState() method adds all changes relating to the component state and resets React to render the component and its children accordingly.
To change the state object of a component, use the setState() method. That way, the component will know it has changed so it will call the render() method appropriately. When updating the UI, this is the best method to use.
Syntax
Parameters
updater
A function with the signature: (state, props) => stateChange.
state reflects the component's current, up-to-date state and the function returns it.
callback
Upon updating the state, you can specify a callback function.
Rules of Using setState( )
Rule 1: Try not to change state directly
As shown below, you should never directly change a state variable's value; use a function instead.
Rule 2: State Updates can be asynchronous
Always include a callback function in a state variable update that results in an asynchronous request. Below is an example of code.
Rule 3: Merging state updates
Perform their updates in one function instead of using multiple this.setState() calls. See the example below:
Code Example
The following code will help you understand how to use SetState in your react application.
Use the following command in the root directory of your project to run the application:
Output
Conclusion
Almost every dynamic application involves state management. A React component can manage the state using a simple and flexible API provided by React.
React components can often change state as a result of user actions, network activity, API requests, or specific application behavior.
